how does a car battery work physics
The alternator is a generator whose purpose is to distribute electricity to the car and recharge the battery. A battery is a device that transforms chemical energy to electric energy and that is the basic way a car battery works.

The Mobility Revolution Quantum Physics Based Tech To Cut Ev Charging Time To Nine Seconds Pv Magazine International
July 4 2021.

. As the ions move freely around the lead plates another chemical. To find the power of a car battery we multiply the CCA number by 72 volts. How A Car Battery Works basic working principle.
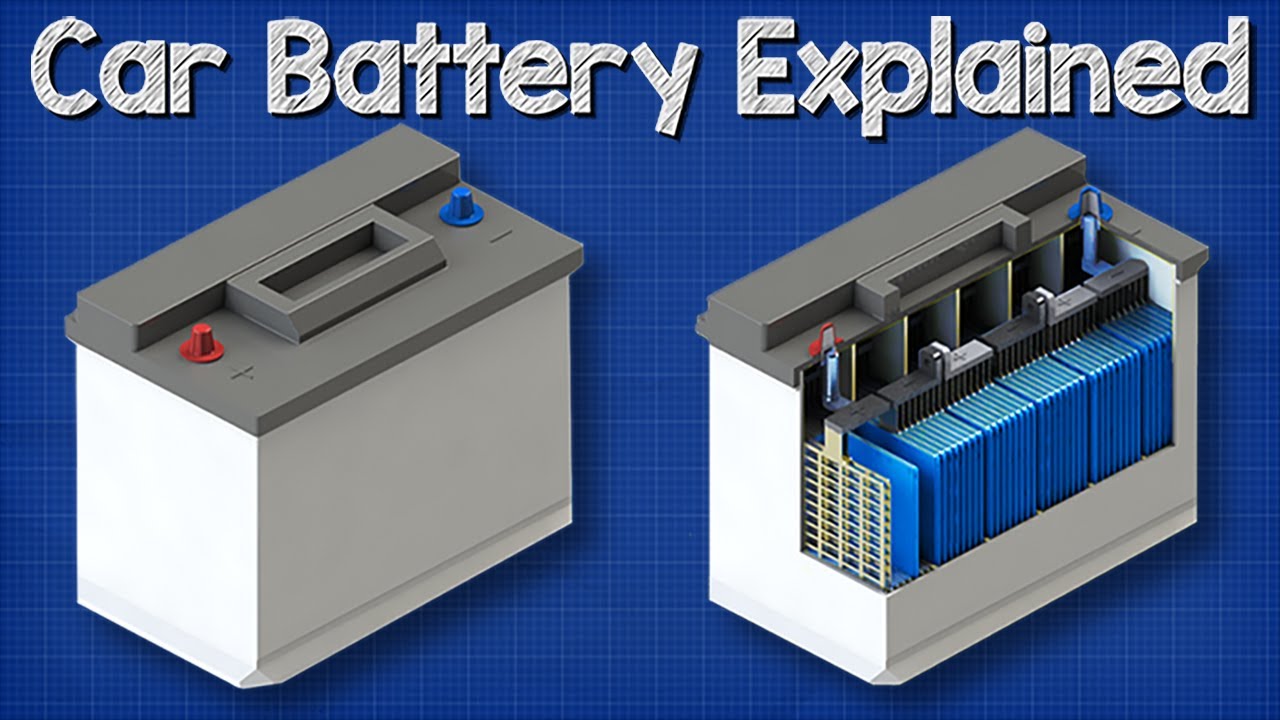
A car battery is actually 6 smaller batteries that are lined up in series. The purpose of the starter motor using the battery is to get the engine moving so that the combustion cycle can be initiated. The car battery produces direct current after a series of reactions within the car battery itself.
They work differently depending on whether they are for the windshield or the rear. Most modern cars require relatively low cold cranking. A car battery uses lead-acid technology to turn chemical energy into electricity.
You can only use power that has a. The combustion cycle is self-sustaining but it relies. How does a car battery work physics.
A typical SLI battery has six cells. This means that it doesnt move. The electrodes in the battery contain atoms of certain conducting materials.
Each cell is able to produce about 2-volts of energy. One is made of lead the other of lead dioxide. Jason Fenske from Engineering Explained explains how flooded lead-acid car batteries work.
As the ions move freely around the lead plates another chemical. The chemical energy results from the lead-acid reaction that begins the. How does a car battery work physics.
The electrical current then flows from the. P 600 A 72 V P 4320 W. These batteries only work in one direction transforming chemical energy to electrical energy.
For instance in an. A car battery uses lead-acid technology to turn chemical energy into electricity. All of the parts of the battery work together to make the flashlight light up.
This causes the voltages of each battery to add. The general way that a battery works is that when an. How Does A Car Battery Work Mach 1 Services.
In physics work is the energy transferred to or from an object via the application of force along a displacement. Heres how the conventional lead-acid liquid cell car battery worksThe purpose of a car battery is to provide electricity to start the engine spark for ign. Defrosters clear condensation from windows and melt frost ice and snow.
If the bad battery is shorted then it. Each cell has two plates or grids. The car battery is made up.
The starter has much less resistance than the bad battery so most of the current will go through the starter allowing a jump start to work. 1 Outside of some hybrid models all vehicles with a standard internal. To learn more about cars and how they work check out Jasons YouT.
The movement of the lithium ions creates free electrons in the anode which creates a charge at the positive current collector. But in other types of batteries the reaction can be reversed. The electrons in the wire that are pumped around the circuit by the battery do move and thus have charge.

21 2 Electromotive Force Terminal Voltage College Physics Chapters 1 17

How A Car Battery Works The Engineering Mindset
How A Car Battery Works Basic Working Principle Youtube

How A Car Battery Works The Engineering Mindset

How Do Electric Cars Work Electric Engines Explained Edf

How Long Do Hybrid Batteries Last

How A Car Battery Works Basic Working Principle Youtube

Solved 5 2 Pts A Typical Car Battery 12v Has About Chegg Com
Physics Relativity Powers Your Car Battery

Bu 201 How Does The Lead Acid Battery Work Battery University
Faraday S Law And Auto Ignition
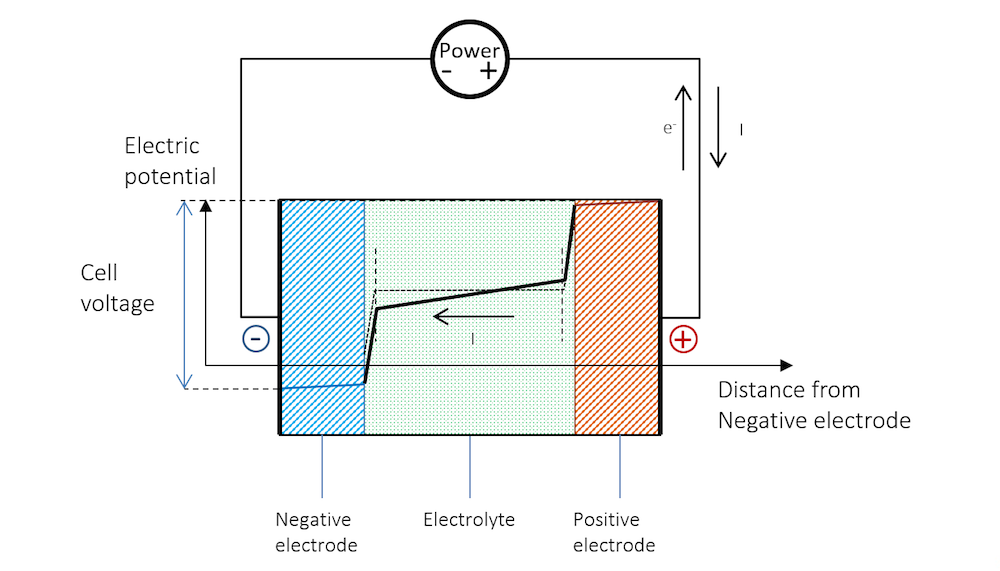
Does The Current Flow Backwards Inside A Battery Comsol Blog

Beyond The Lithium Ion Battery Physics World

How Do Car Batteries Work Kwik Fit
How Does A Car Battery Work And How Is It Constructed

Multi Physics Design Of A New Battery Packaging For Electric Vehicles Utilizing Multifunctional Composites Sciencedirect
